Despite the widespread use of digital technology, handwriting remains a valuable skill with numerous cognitive and developmental advantages.
It engages different brain areas and fosters critical thinking, creativity, and memory retention. In an era of digital shortcuts, handwriting enhances learning and preserves individuality.
Read on to discover the neuroscience behind handwriting and how it can improve memory retention, cognitive function, and overall learning outcomes.
Table of Contents
- 1. The Importance of Handwriting in The Digital Age
- 2. Handwriting vs. Typing
- 3. The Neuroscience of Handwriting
- 3.1. How Handwriting Activates Multiple Brain Regions
- 3.2. The Role of Fine Motor Skills in Memory Retention
- 3.3. The Connection Between Handwriting and Long-Term Memory
- 4. The Impact of Ink Color on Learning and Memory Retention
- 4.1. The Psychology of Color and its Impact on Cognition
- 4.2. How Different Ink Colors Can Affect Mood and Focus
- 4.3. Studies on the Effects of Black and Blue Ink on Memory Recall
- 4.4. Choosing the Right Ink Color for Optimal Learning and Retention
- 5. Improving Your Handwriting
1. The Importance of Handwriting in The Digital Age
Handwriting continues to be a valuable skill despite the widespread use of digital technology, owing to its many cognitive and developmental advantages.
Handwriting engages different brain areas and stimulates neural pathways, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and memory retention.
Furthermore, it serves as a personal and intimate form of communication, allowing individuals to express themselves uniquely through their penmanship.
Check out our guide, Handwriting vs. Technology: 6 Reasons Why Taking Notes by Hand Still Wins.
In an era where digital shortcuts frequently create impersonal and standardized interactions, we cannot underestimate the significance of handwriting in enhancing learning and preserving individuality.
2. Handwriting vs. Typing
Regarding note-taking and learning, handwriting has distinct advantages over typing. We covered this in-depth in our guide Note Taking Handwriting vs. Typing.
Handwriting activates cognitive processes more effectively than typing, enhancing memory retention and comprehension.
When we handwrite notes, we are involved in a more active learning process, as we need to process and condense the information rather than merely transcribing it verbatim.
This act of processing and summarizing handwritten notes aid in solidifying the information in our minds, resulting in better understanding and recall.
A study by Anne Mangen and Jean-Luc Velay, published in the journal Advances in Haptics, found that participants who took handwritten notes demonstrated superior memory retention and conceptual understanding compared to those who typed notes.
The researchers posited that the tactile experience of handwriting stimulates the brain differently than typing, fostering deeper information processing and ultimately enhancing learning outcomes.
3. The Neuroscience of Handwriting
3.1. How Handwriting Activates Multiple Brain Regions
Handwriting also engages multiple brain regions, providing a more holistic learning experience than typing.
Writing by hand, we simultaneously activate the motor, visual, and language-processing centers.
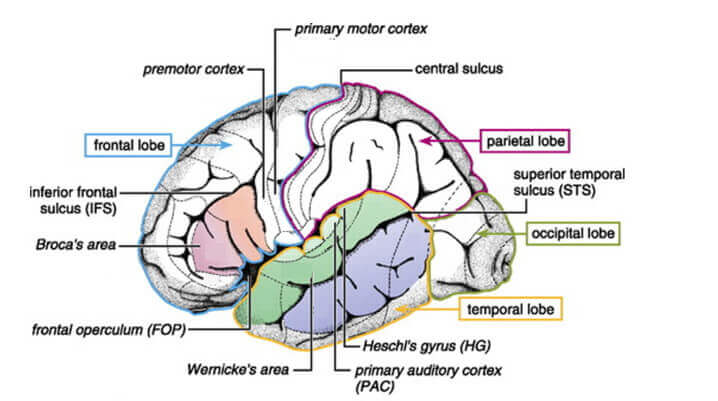
This interconnected activation is known as the “writing triangle,” which involves the motor cortex, the Broca’s area responsible for language production, and the parietal lobe responsible for processing sensory information.
According to a study by Dr. Karin James at Indiana University, the neural activity associated with handwriting promotes the formation of more robust neural pathways, thereby enhancing memory and learning.
Forming letters and words on paper stimulates the brain’s sensorimotor system, strengthening the connection between our cognitive and motor skills.
This multisensory engagement fosters better information retention and contributes to developing fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination.
3.2. The Role of Fine Motor Skills in Memory Retention
Fine motor skills are critical in memory retention, particularly in handwriting.
Forming letters and words on paper requires fine motor skills, which involve coordinating small muscle movements in the hands, fingers, and wrists.
This process engages the brain’s sensorimotor system, strongly linking cognitive and motor functions.
According to research by Dr. Virginia Berninger [PW1] at the University of Washington, students who write by hand demonstrate better recall and understanding of the material than those who type.
Dr. Berninger attributes it to handwriting requires the generation of unique letterforms, which stimulate the brain’s sensorimotor system and reinforce the connections between motor skills and cognitive processes.
As a result, handwriting fosters improved memory retention and overall learning.
3.3. The Connection Between Handwriting and Long-Term Memory
The connection between handwriting and long-term memory is particularly noteworthy.
When we write by hand, we engage in a complex, multisensory process that requires the brain to coordinate various cognitive, motor, and perceptual systems.
This deep brain involvement during handwriting strengthens neural connections, enhancing our ability to encode, store, and retrieve information in long-term memory.
In a study by Pam A. Mueller and Daniel M. Oppenheimer, participants who took handwritten notes demonstrated a better understanding of the material and could recall more information than those who typed their notes.
We attributed this to the fact that handwriting involves generating unique letterforms, which promote deeper processing and better consolidation of information. Moreover, writing by hand makes us more likely to summarize and paraphrase information.
4. The Impact of Ink Color on Learning and Memory Retention

4.1. The Psychology of Color and its Impact on Cognition
The psychology of color significantly shapes our cognitive processes, influencing our emotions, perceptions, and even our memory functions.
Colors can evoke different psychological responses that enhance or hinder our cognitive abilities.
For instance, research has demonstrated that colors like blue and green can calm the mind and promote creativity.
In contrast, warmer colors, such as red and yellow, can stimulate attention and increase alertness.
Moreover, colors can also affect memory retention, as they can serve as cues that facilitate the encoding and retrieval of information.
In a Juliet Zhu and Ravi Mehta study, participants exposed to blue-colored environments exhibited increased creativity.
In contrast, those exposed to red-colored environments showed enhanced attention to detail.
These findings suggest that color can significantly impact cognitive processes, making it an essential factor when selecting writing instruments or designing learning environments.
Colors can also impact motivation and productivity, further highlighting the importance of understanding the psychological effects of color on cognition.
By carefully selecting colors conducive to learning and memory retention, we can create environments that maximize our cognitive potential and promote more effective learning experiences.
4.2. How Different Ink Colors Can Affect Mood and Focus
Different ink colors can profoundly impact our mood, focus, and cognitive performance.
Writing with various ink colors can trigger specific emotional responses, influencing our ability to concentrate, think creatively, and retain information.
For instance, writing with blue ink has been associated with feelings of calmness and relaxation, which can promote a conducive environment for creative thinking and problem-solving.
On the other hand, using red ink can evoke a sense of urgency and alertness, enhancing attention to detail and analytical thinking.
These emotional responses to different ink colors can also affect our level of focus and productivity.
For example, when we write with colors that align with the task, we are more likely to maintain our concentration and perform at our best.
For example, using blue ink when brainstorming new ideas can help facilitate a creative mindset, while red ink can be more suitable for tasks that require precision and accuracy.
Furthermore, experimenting with various ink colors can help maintain our interest and engagement in the task, preventing boredom and promoting better information retention.
By being mindful of different ink colors’ emotional and cognitive impact, we can make informed decisions on which colors to use for specific tasks, ultimately enhancing our learning and productivity.
4.3. Studies on the Effects of Black and Blue Ink on Memory Recall
Several studies have investigated the effects of black and blue ink on memory recall, with some interesting findings.
For example, researchers have found that blue ink might enhance memory retention and recall compared to black ink.
For example, one study by the University of British Columbia suggested that people exposed to the color blue were likelier to perform better on creative tasks. In contrast, those exposed to red had better performance on detail-oriented tasks.
This finding indicates that using blue ink could stimulate the brain’s creative centers, thus improving memory recall for the written material.
Another study published in the journal Consciousness and Cognition revealed that using a blue pen helped participants recall more words from a list when compared to a black pen.
The researchers hypothesized that the blue ink might have increased the participants’ arousal levels, making the information more memorable.
Although more research is needed to establish a definitive link between ink color and memory recall, these studies suggest that blue ink may benefit memory retention and creative thinking.
4.4. Choosing the Right Ink Color for Optimal Learning and Retention
Choosing the right ink color for optimal learning and retention is essential, as it can significantly influence your cognitive processes and memory recall.
While black ink has long been the standard for formal writing, blue ink may provide unique advantages for learning and creativity.
As mentioned earlier, studies have demonstrated that blue ink can enhance memory recall and stimulate creative thinking.
Additionally, blue ink may help increase focus and create a calming effect on the mind, further aiding in retaining information.
Therefore, when taking notes or engaging in tasks that require learning and memorization, consider using blue ink to improve your cognitive performance potentially.
However, it is essential to note that individual preferences and experiences may vary; finding the ink color that works best for you may require some experimentation.
Ultimately, the right ink color for optimal learning and retention depends on your unique needs and specific tasks.
5. Improving Your Handwriting
Improving your handwriting is a great way to enhance your learning and memory retention.
With our guides, “7 Steps to Better Handwriting” and “Write Faster and Neater in 6 Simple Steps,” you can learn the techniques and exercises necessary to improve your penmanship.
Additionally, if you want to improve your speed while maintaining neatness, “Speed Writing Essentials Choosing the Perfect Pen ” is an excellent resource.
And “The Best 3 Pens for Fast Handwriting” ensure you have the right Pen to achieve your handwriting goals.
With these resources, you can continue to reap the benefits of handwriting and take your skills to the next level.
5.1. Conclusion
In conclusion, despite the rise of digital technology, handwriting offers significant cognitive and developmental benefits.
Choosing the right ink color can make a big difference in enhancing learning and retention. While black ink is a traditional choice, blue ink has unique advantages for learning and creativity.
Experimenting with different colors can help you find the perfect fit for your needs.
By considering the emotional and cognitive impact of different ink colors, you can make the most informed decisions and maximize your learning and productivity.
